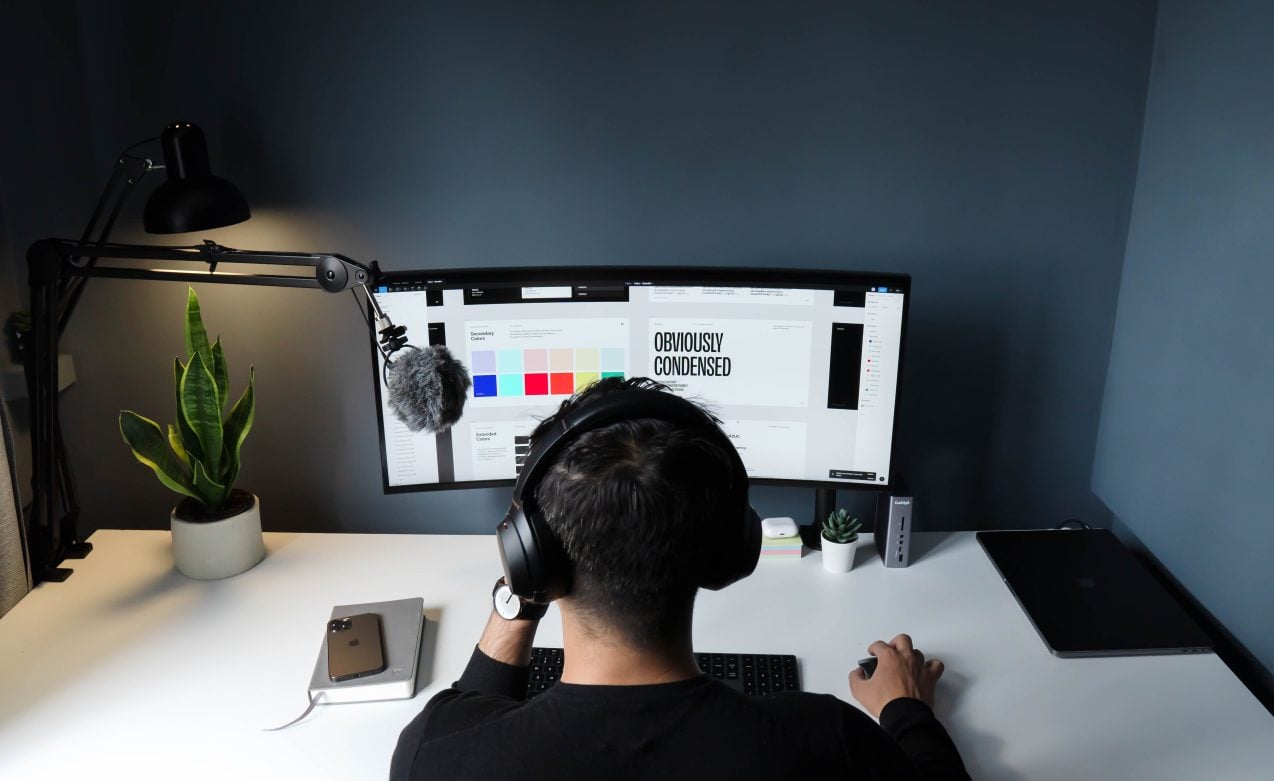
Organizational preferences appear to be shifting towards a renewed support for the traditional in-office work paradigm, in sharp contrast to the common belief that remote work increases productivity and quality. Recent studies outline a situation in which employees place a high value on the freedom that comes with remote work, but where companies are increasingly showing a preference for more typical office ecosystems.
The University of Chicago's Becker Friedman Institute's study reveals a significant finding: workers who don't have to drive to and from work gain a valuable extra hour every day. However, the persistence of certain companies in orchestrating a reversion of employees to traditional office spaces warrants an exploration into the underlying motivations steering this inclination.
TheParadigm 2022 Hiring Benchmark Report from Criteria unveils a direct correlation between the imposition of in-office work mandates and a surge in employee turnover rates. This strategic subtlety serves as an expedient maneuver for organizations navigating the realms of downsizing, allowing for a nuanced reduction in workforce without the blatant execution of layoffs. This operational pattern is visibly manifested in the corporate articulations of companies such as Lyft and Amazon, characterized by announcements embodying a fusion of layoffs and mandates for office returns. Elon Musk's acquisition of Twitter also reflects comparable operational tendencies, marked by a synergy of mandated office returns and ensuing layoffs.
An exploration by Microsoft into remote work paradigms during the pandemic era depicts the emergence of more segregated and collaboration-deficient employee factions. The enhancement in email communication fails to negate the prevailing challenges in navigating intricate informational exchanges in remote settings. This sentiment is echoed by an array of CEOs including Amazon’s Andy Jassy, Goldman Sachs’ David Solomon, and Disney’s Bob Iger, all underscoring the indispensable nature of direct interpersonal interactions and collaborations in fostering innovation.
The psyche of managerial entities in the hybrid work model, as per a 2022 study by Microsoft, is fraught with pervasive skepticism, with a substantial 85% grappling with reservations regarding the actualization of work by employees in the absence of traditional productivity indicators. The turn to surveillance methodologies by companies, as highlighted by an ExpressVPN study, is emerging as a prevalent strategy to mitigate uncertainties surrounding employee activities, with the majority of surveyed entities confessing to a trust deficit in employee productivity in unsupervised settings. https://www.lapost.com/find-out-if-your-state-gets-the-most-federal-funding/
The apparent benefits of remote work notwithstanding, there seems to be a discernible shift in organizational preferences leaning towards the re-embrace of traditional office settings. This resurgence seems to be driven by a conglomerate of factors including strategic downsizing nuances, collaboration impediments, and the prevailing skepticism entrenched within leadership echelons, steering the momentum towards conventional workplace norms.

 Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
 Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
 Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
 You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
 Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
 Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness
Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness