In chemistry, structure is everything. Compounds with the same chemical formula can have different properties depending on the arrangement of the molecules they’re made of. And compounds with a different chemical formula but a similar molecular arrangement can have similar properties.
Graphene and a form of boron nitride called hexagonal boron nitride fall into the latter group. Graphene is made up of carbon atoms. Boron nitride, BN, is composed of boron and nitrogen atoms. While their chemical formulas differ, they have a similar structure – so similar that many chemists call hexagonal boron nitride “white graphene.”
Carbon-based graphene has lots of useful properties. It’s thin but strong, and it conducts heat and electricity very well, making it ideal for use in electronics.
Similarly, hexagonal boron nitride has a host of properties similar to graphene that could improve biomedical imaging and drug delivery, as well as computers, smartphones and LEDs. Researchers have studied this type of boron nitride for many years.
But, hexagonal boron nitride isn’t the only useful form this compound comes in.
As materials engineers, our research team has been investigating another type of boron nitride called cubic boron nitride. We want to know if combining the properties of hexagonal boron nitride with cubic boron nitride could open the door to even more useful applications.
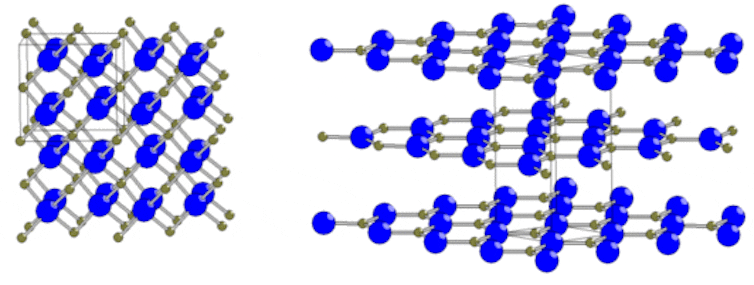
Hexagonal versus cubic
Hexagonal boron nitride is, as you might guess, boron nitride molecules arranged in the shape of a flat hexagon. It looks honeycomb-shaped, like graphene. Cubic boron nitride has a three-dimensional lattice structure and looks like a diamond at the molecular level.
H-BN is thin, soft and used in cosmetics to give them a silky texture. It doesn’t melt or degrade even under extreme heat, which also makes it useful in electronics and other applications. Some scientists predict it could be used to build a radiation shield for spacecraft.
C-BN is hard and resistant. It’s used in manufacturing to make cutting tools and drills, and it can keep its sharp edge even at high temperatures. It can also help dissipate heat in electronics.
Even though h-BN and c-BN might seem different, when put together, our research has found they hold even more potential than either on its own.
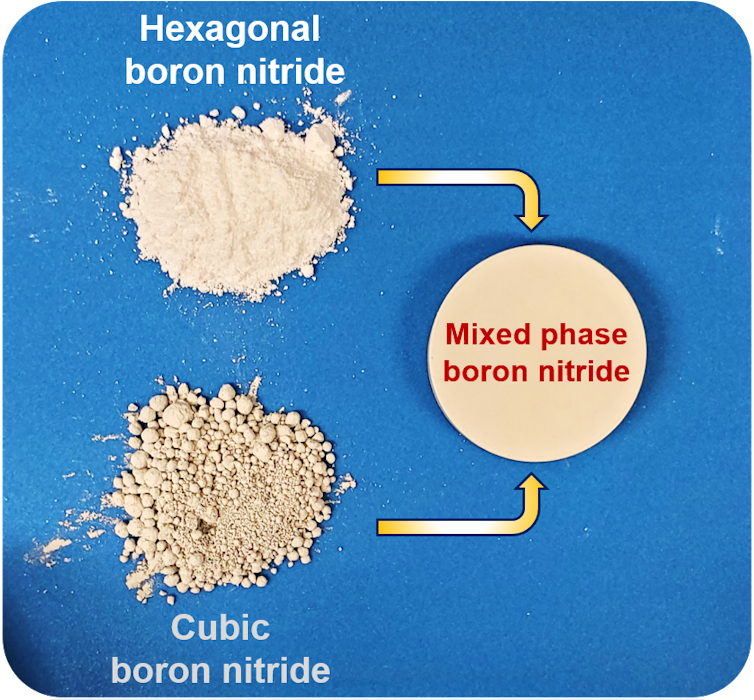

Both types of boron nitride conduct heat and can provide electrical insulation, but one, h-BN, is soft, and the other, c-BN, is hard. So, we wanted to see if they could be used together to create materials with interesting properties.
For example, combining their different behaviors could make a coating material effective for high temperature structural applications. C-BN could provide strong adhesion to a surface, while h-BN’s lubricating properties could resist wear and tear. Both together would keep the material from overheating.
Making boron nitride
This class of materials doesn’t occur naturally, so scientists must make it in the lab. In general, high-quality c-BN has been difficult to synthesize, whereas h-BN is relatively easier to make as high-quality films, using what are called vapor phase deposition methods.
In vapor phase deposition, we heat up boron and nitrogen-containing materials until they evaporate. The evaporated molecules then get deposited onto a surface, cool down, bond together and form a thin film of BN.
Our research team has worked on combining h-BN and c-BN using similar processes to vapor phase deposition, but we can also mix powders of the two together. The idea is to build a material with the right mix of h-BN and c-BN for thermal, mechanical and electronic properties that we can fine-tune.
Our team has found the composite substance made from combining both forms of BN together has a variety of potential applications. When you point a laser beam at the substance, it flashes brightly. Researchers could use this property to create display screens and improve radiation therapies in the medical field.
We’ve also found we can tailor how heat-conductive the composite material is. This means engineers could use this BN composite in machines that manage heat. The next step is trying to manufacture large plates made of a h-BN and c-BN composite. If done precisely, we can tailor the mechanical, thermal and optical properties to specific applications.
In electronics, h-BN could act as a dielectric – or insulator – alongside graphene in certain, low-power electronics. As a dielectric, h-BN would help electronics operate efficiently and keep their charge.
C-BN could work alongside diamond to create ultrawide band gap materials that allow electronic devices to work at a much higher power. Diamond and c-BN both conduct heat well, and together they could help cool down these high-power devices, which generate lots of extra heat.
H-BN and c-BN separately could lead to electronics that perform exceptionally well in different contexts – together, they have a host of potential applications, as well.
Our BN composite could improve heat spreaders and insulators, and it could work in energy storage machines like supercapacitors, which are fast-charging energy storage devices, and rechargeable batteries.
We’ll continue studying BN’s properties, and how we can use it in lubricants, coatings and wear-resistant surfaces. Developing ways to scale up production will be key for exploring its applications, from materials science to electronics and even environmental science.

Pulickel Ajayan receives funding from the Army Research Laboratory and the Army Research Office.
Abhijit Biswas does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Source: The Conversation

 Russian oil firm shrugs off sanctions, insurer says dodgy operators will profit
Russian oil firm shrugs off sanctions, insurer says dodgy operators will profit
 Senior UK lawmaker flags concerns about Shein to LSE and regulator
Senior UK lawmaker flags concerns about Shein to LSE and regulator
 BofA bets on a potential Fed rate hike after jobs report, top Wall-St brokers revise forecasts
BofA bets on a potential Fed rate hike after jobs report, top Wall-St brokers revise forecasts
 Greenland leader says everyone should respect island's wish for independence
Greenland leader says everyone should respect island's wish for independence
 Italy foreign minister proposes setting aside EU sanctions on Syria
Italy foreign minister proposes setting aside EU sanctions on Syria
 Judge extends Megan Thee Stallion’s protection order against rapper Tory Lanez until 2030
Judge extends Megan Thee Stallion’s protection order against rapper Tory Lanez until 2030
 Lamar Jackson repeats and Ja’Marr Chase and Justin Jefferson are unanimous choices for AP All-Pro
Lamar Jackson repeats and Ja’Marr Chase and Justin Jefferson are unanimous choices for AP All-Pro
 How a loss to Northern Illinois set the table for Notre Dame's run to the CFP title game
How a loss to Northern Illinois set the table for Notre Dame's run to the CFP title game
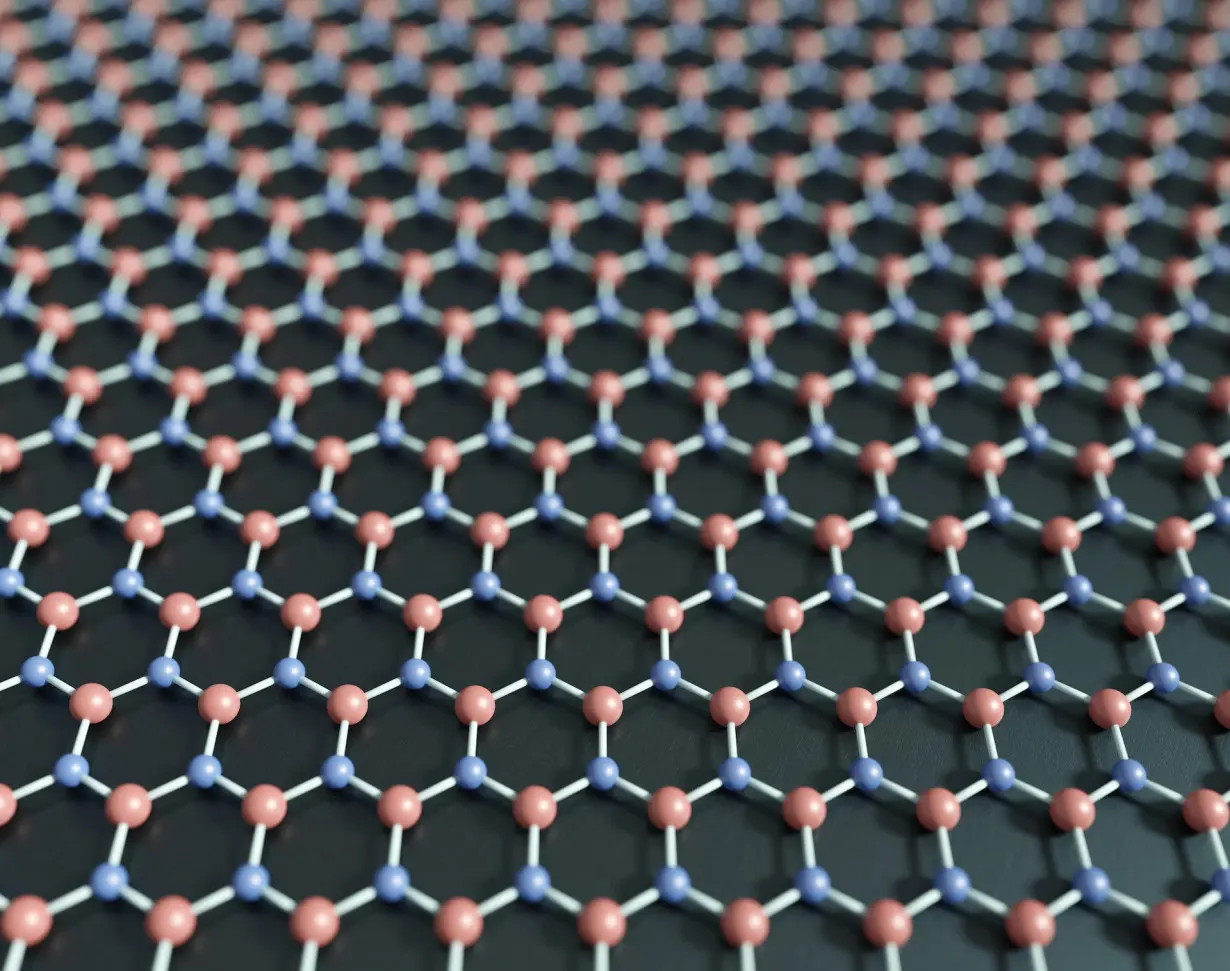 Hexagonal boron nitride, also known as
Hexagonal boron nitride, also known as