By Will Dunham
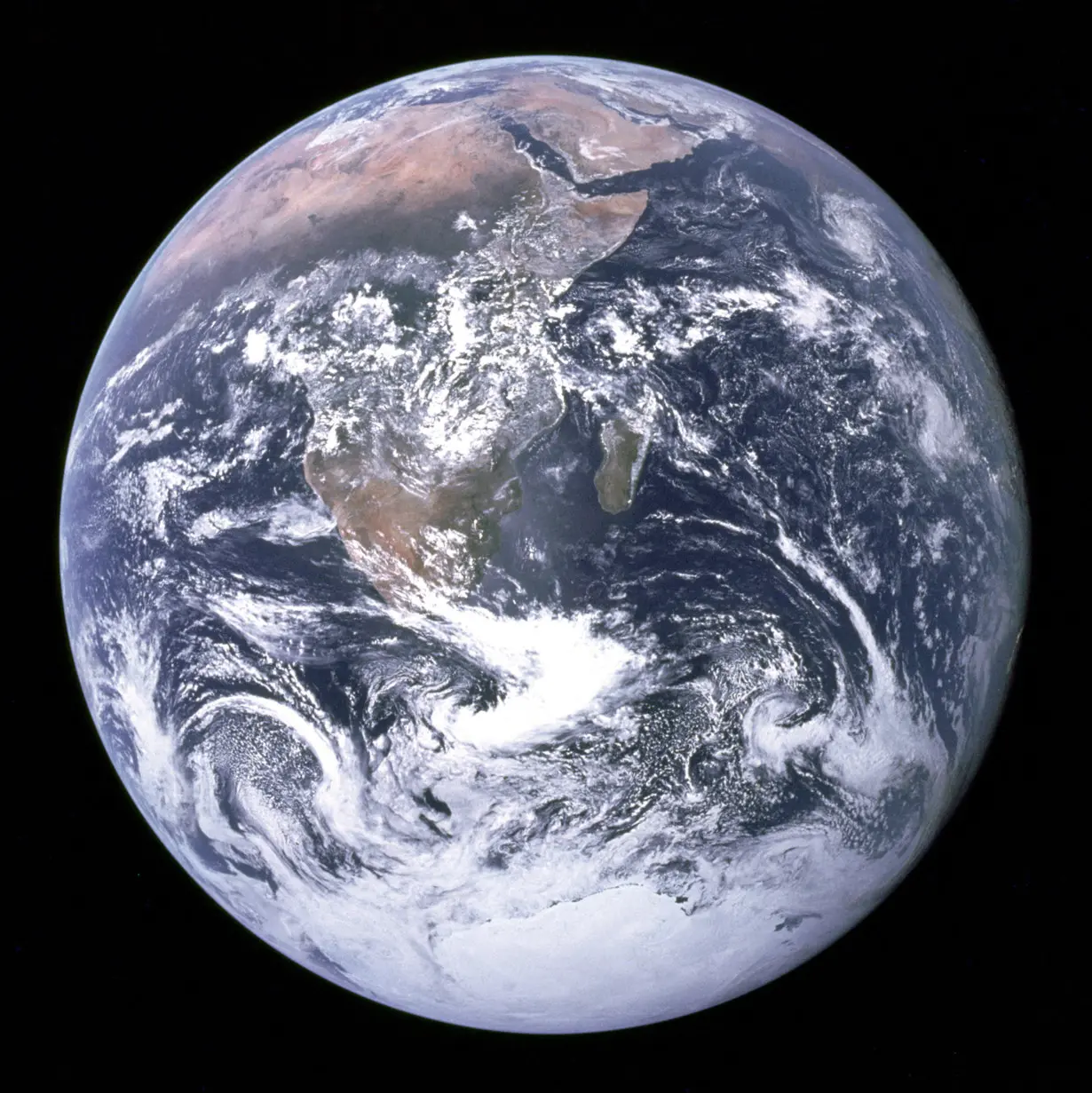
WASHINGTON (Reuters) - Seismologists have recognized since the 1970s that two mysterious continent-sized blobs reside in the deepest part of Earth's mantle, one under Africa and the other under the South Pacific region.
These blobs, denser than the material surrounding them, may be relics from a cataclysm early in our planet's history hypothesized to have spawned the moon - the collision between primordial Earth and a Mars-sized object called Theia, researchers said on Wednesday.
This giant impact, which recent research determined occurred 4.46 billion years ago, blasted molten rock into space that orbited Earth and coalesced into the moon. But chunks of Theia may have remained inside Earth, sinking to a location just above our planet's wickedly hot spherical core of iron and nickel.
The researchers ran computer simulations examining the impact event, geophysical properties of the material that likely made up Theia and the evolution of Earth's mantle - the broadest of the layers that comprise our planet's interior structure at about 1,800 miles (2,900 km) thick.
Based on these simulations, they proposed that most of Theia was absorbed into Earth, forming the blobs, while residual debris formed the moon.
"The bottoms of these blobs are 2,900 kilometers below our feet. The two blobs are about 2% of Earth's mass. They were detected by seismology as seismic waves travel slower within these two regions compared to the surrounding mantle. Each of the blobs are twice the mass of the whole moon. So, the blobs are massive," said Caltech geophysicist Qian Yuan, lead author of the study published in the journal Nature.
If the study's conclusions are correct, these blobs would represent the first direct evidence of the hypothesized moon-forming collision.
"There hasn't been much consensus on whether we can find evidence for this event not just in the moon but also in some observable property of the modern Earth," Caltech geology and geochemistry professor and study co-author Paul Asimow said.
The two blobs, Asimow added, "are the biggest deviations in Earth structure from a simple layered planet."
"It is incredible because we can uncover relics of another planet - Theia - if we dig deep enough in Earth's mantle," added planetary scientist and study co-author Hongping Deng of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Shanghai Astronomical Observatory.
The increased density of the blobs is thought to arise from their high level of iron - much like moon rocks, which would make sense if they are made of the same source material from Theia.
"After the impact, these impactor materials would sink down to the core-mantle boundary because they likely have higher density than ambient mantle, and it is the extra density that allows them to survive Earth's whole history," Yuan said.
The moon, which orbits Earth at an average distance of about 239,000 miles (385,000 km), has a diameter of about 2,160 miles (3,475 km), a bit more than a quarter of our planet's diameter.
Asimow said that if their conclusions are correct some volcanic rocks that reach Earth's surface may provide samples of a vanished planet.
"If our model is correct, the blobs should have isotopes - trace elements - that are similar to the lunar mantle rocks, which can be tested in future lunar missions," Yuan said.
Gaining a greater understanding of the hypothesized giant impact may provide insight concerning the evolution of Earth and other rocky planets in our solar system and beyond.
"We suspect that large impacts are common in the later stages of accretion of all terrestrial (rocky) planets and exoplanets," Asimow said. "As we try to develop a catalog of what the possible outcomes of planet formation are - how likely is a planet like Earth, rather than like Mars, Mercury, Venus or none of the above, and hence how likely are we to find other Earth-like planets - it follows that we need to work out the consequences of these impacts."
(Reporting by Will Dunham, Editing by Rosalba O'Brien)

 Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
 Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
 Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
 You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
 Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
 Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness
Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness