(CNN) — Paleobiologist Dr. Kenshu Shimada has been fascinated by fossil sharks, including the giant Otodus megalodon, since childhood — he found his first megalodon tooth at 13 years old. So when he saw the 2018 blockbuster “The Meg,” he thought something was fishy. Not only did the movie depict the long-extinct megalodon surviving to modern times, but the 75-foot-long (23-meter-long) Hollywood version of the predator seemed way too big.
Exactly how large megalodon was in real life is a long-standing mystery — no complete fossils have ever been discovered. But now, to Shimada’s own surprise, his most recent research suggests megalodon could have reached a whopping length of 80 feet (24 meters).
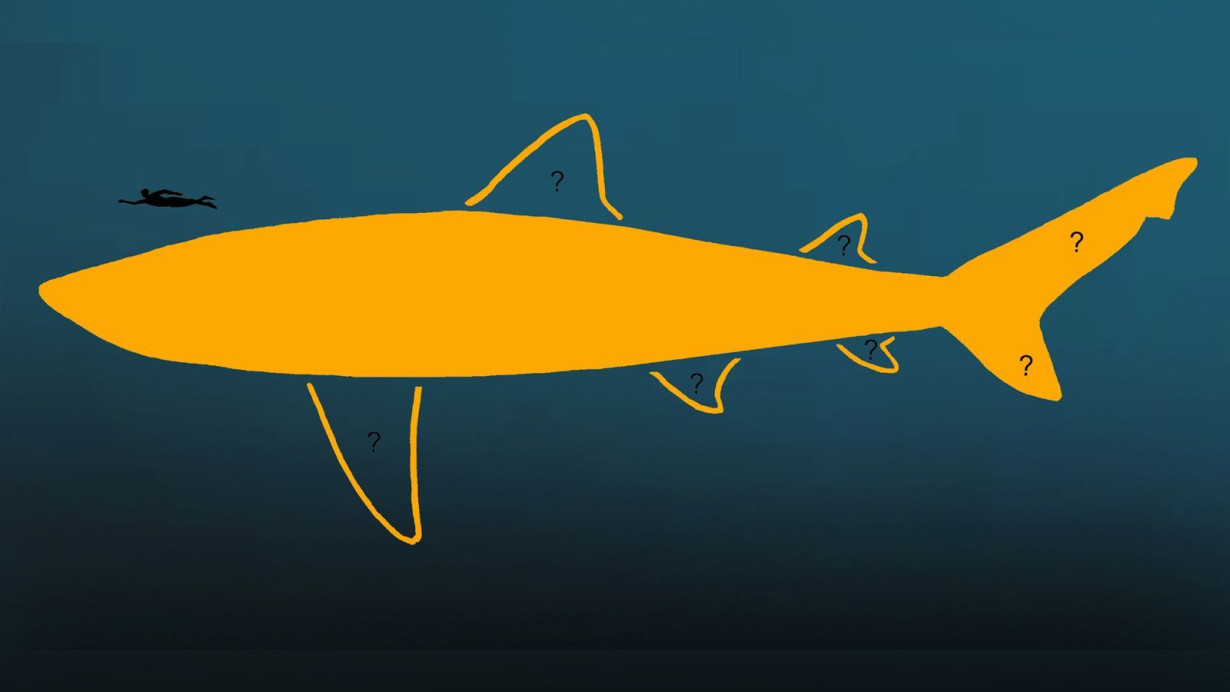
What’s more, he and his coauthors posit that megalodon was slenderer than previously thought, closer in build to a sleek lemon shark than a chunky great white, according to the study published Sunday in the journal Palaeontologia Electronica.
“Megalodon is not a simple, gigantic version of great white shark. I think that we really have to move away from that concept,” said Shimada, a professor of biological and environmental sciences at DePaul University in Chicago who served as lead author.
The findings could help reshape how scientists and popular science fiction depict the enormous creature — and has possibly shed light on what lets some marine vertebrates evolve extraordinarily huge proportions, according to Shimada.
Megalodon fossil record: Plenty of teeth but not much else
Unlike in “The Meg,” the prehistoric megalodon never coexisted with humans, but between 15 million and 3.6 million years ago, the apex predator dominated oceans around the world, according to various megalodon fossils scientists have unearthed.
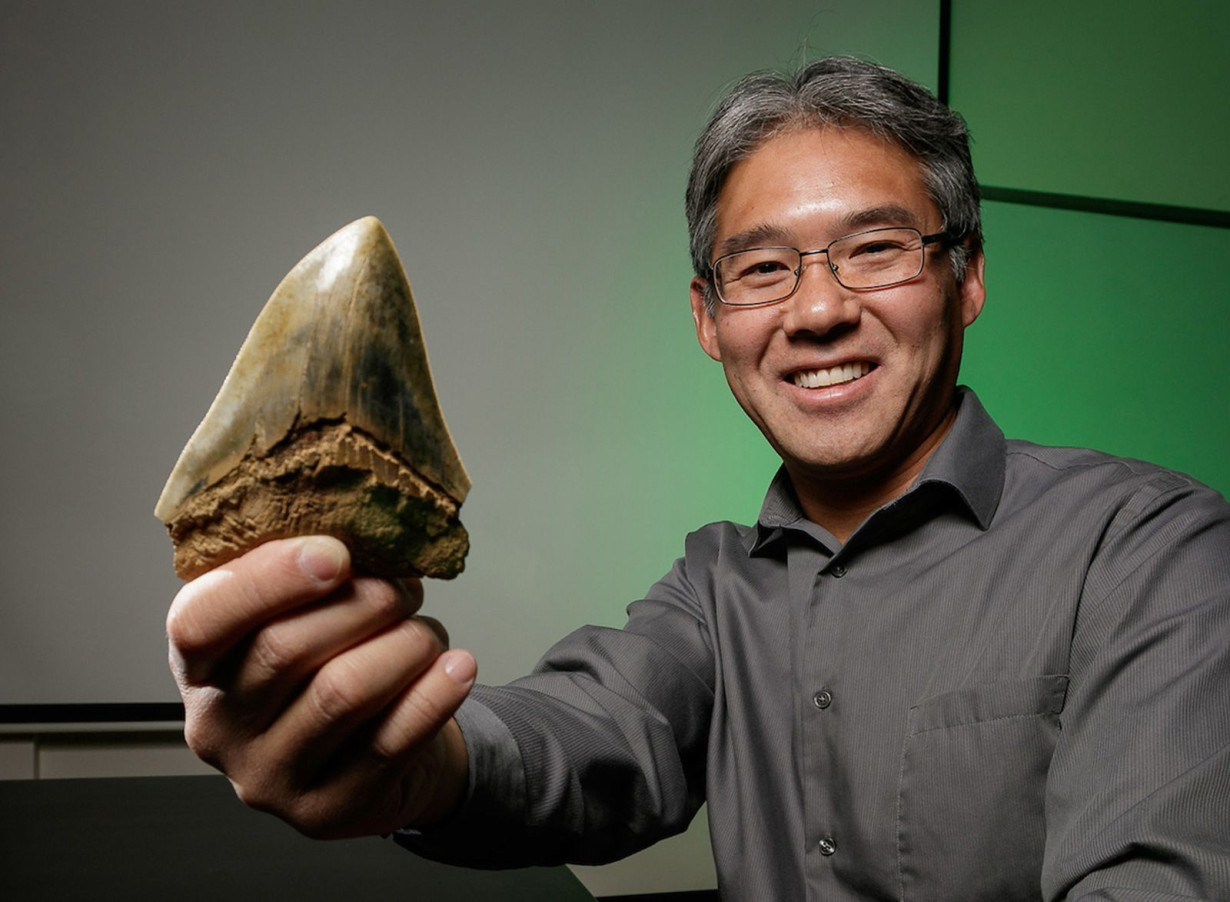

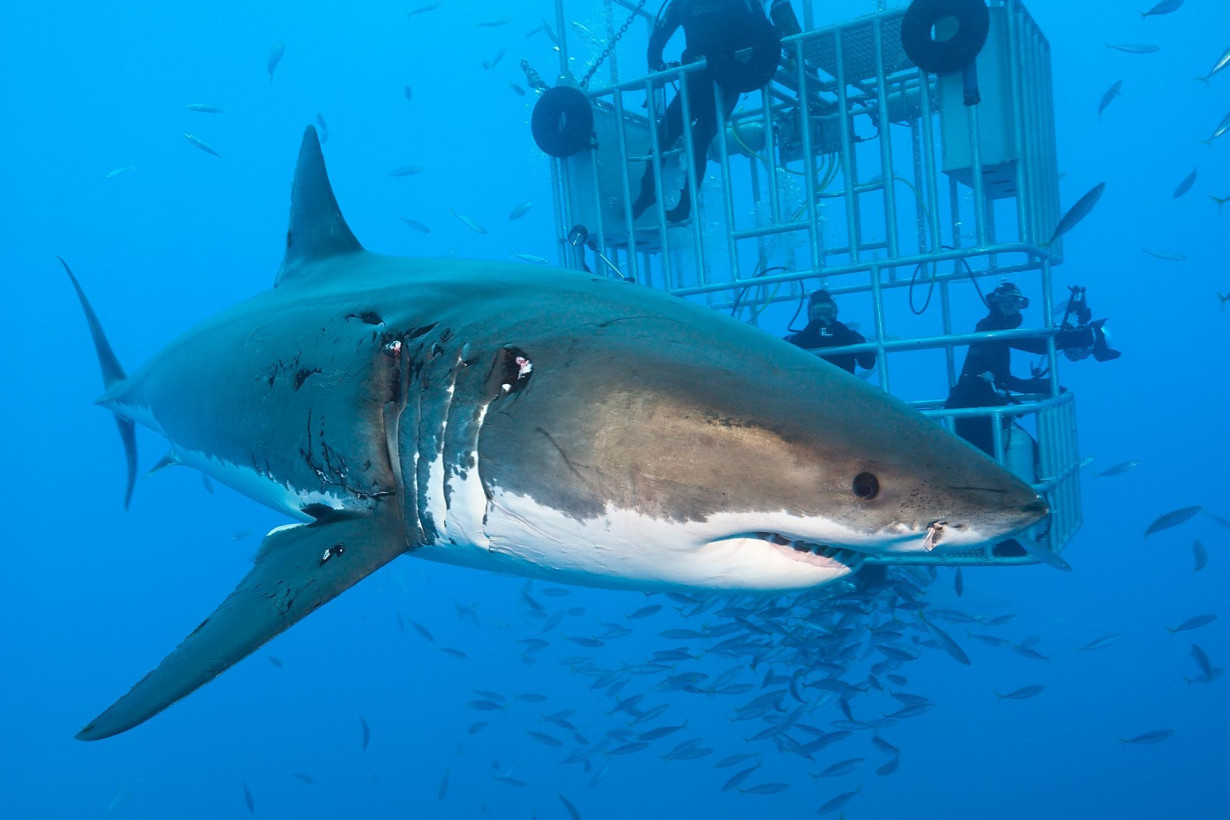
As a shark, megalodon is part of the family of cartilaginous fishes. “They have a very poorly mineralized skeleton. There are no true bones that make the skeleton hard,” Shimada said. “On the other hand, teeth are very hard, so they’re durable.” Megalodon produced new teeth throughout its life, helping make these fossils a fairly common find.
Along with teeth, the existing fossil record includes parts of giant shark skeletons from the same period, including a 36-foot-long (11-meter-long) section of a fossilized spinal column from Belgium, a news release stated.
The vertebrae of this shark are up to 6 inches (15 centimeters) in diameter; another fossil shark specimen from Denmark has vertebrae that are 9 inches (23 centimeters) across. For context, adult human vertebrae are roughly 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter.
Neither shark backbone specimens were found with the massive, serrated teeth associated with megalodon, but scientists have presumed they belong to the same species.
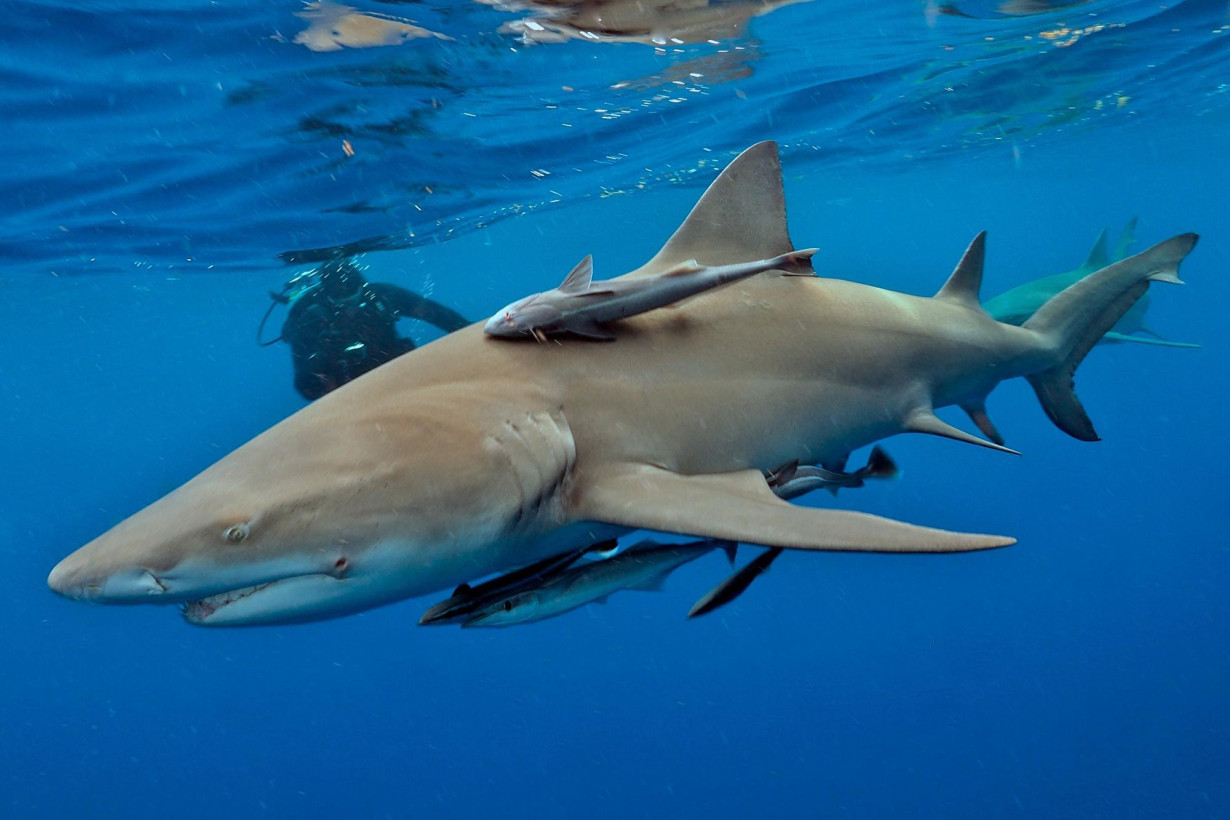

Megalodon’s teeth resemble those of a modern great white shark, so some scientists previously concluded that the two sharks had a similar stout body shape. Shimada followed this hypothesis when he published a paper in September 2019, arguing that the maximum size for megalodon was “just” 50 feet (15.3 meters) long.
However, several years ago, Shimada and some of his colleagues began to question the underlying assumption that megalodon looked like a huge great white shark. In reviewing a August 2022 paper, in which scientists built a digital 3D model of megalodon, Shimada found some of the math behind the shark’s proportions didn’t seem to add up.
“We kind of realized — click— that (the) great white shark is not a good model,” Shimada said. So, he began searching for a better match for megalodon’s modern analogue.
Megalodon may have had a long, sleek body
Shimada and his team compared 145 species of living sharks and 20 species of extinct sharks and built a database of the proportions of their heads, bodies and tails. The researchers then compared these proportions with the parts of megalodon’s body that have been found.
“We have a vertebral column that’s known, and if we assume that that’s the complete trunk length, then why can’t we estimate the head length and a tail length based on modern day?” Shimada said.
The researchers calculated that the likeliest body plan for megalodon wouldn’t have been that of a stout, tanklike great white but rather a more streamlined fish, such as a lemon shark. In this discovery, Shimada said, his team also stumbled upon a larger pattern in marine biology.
“Inadvertently, we discovered the mystery of why some vertebrates can get large, but some cannot,” Shimada said. Great white sharks, with their thick bodies that grow to about 20 feet long (6 meters), seem to be about as big as a stocky animal can be and still move efficiently through the water. Meanwhile, sleeker animals such as blue whales, which can grow up to about 100 feet (30 meters) long, can attain enormous lengths while still swimming well.
“If you stay in a skinnier body, there is a better chance of being able to grow larger,” Shimada said. This principle applies to megalodon, which according to Shimada’s new study could have been up to 80 feet (24 meters) long, but thinner than previous models.
Dr. Stephen Godfrey, the curator of paleontology at the Calvert Marine Museum in Solomons, Maryland, who was not involved with the study, said he was surprised by both megalodon’s proposed similarity to a lemon shark and by the giant size proposed by Shimada and his team.
“The argument that they make, that a long, slender animal that size is more hydrodynamically efficient than if they’re really kind of fat and chunky, like if you scale up a living great white — that argument is a good one,” he said. “But still, I’m not saying it gets stuck in my craw, but wow. I mean, that’s twice the size,” Godfrey said, referring to the estimated megalodon length increasing from 50 to 80 feet.
Ultimately, there’s just one way to know for certain how long megalodon was and what it looked like. “What we really need is the discovery of the complete skeleton,” Shimada said. “The real test comes when we really have the complete skeleton, and then it will support or refute whether it was really skinny or stocky.”
The-CNN-Wire
™ & © 2025 Cable News Network, Inc., a Warner Bros. Discovery Company. All rights reserved.

 Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
Trump has begun another trade war. Here's a timeline of how we got here
 Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
Canada's leader laments lost friendship with US in town that sheltered stranded Americans after 9/11
 Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
Chinese EV giant BYD's fourth-quarter profit leaps 73%
 You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
You're an American in another land? Prepare to talk about the why and how of Trump 2.0
 Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
Chalk talk: Star power, top teams and No. 5 seeds headline the women's March Madness Sweet 16
 Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness
Purdue returns to Sweet 16 with 76-62 win over McNeese in March Madness